
India’s National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) is on a mission to expand and modernize the nation’s road network. By unlocking the inherent value in completed highway projects, NHAI aims to create a sustainable funding cycle for future development, reducing reliance on traditional budgetary allocations
NHAI primarily employs two powerful models for asset monetization: Toll-Operate-Transfer (ToT) and Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs). Each offers distinct advantages and caters to different investor appetites.
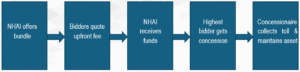
The ToT model involves granting concessionaires (ToT concessionaires are infrastructure players/investors with prior O&M experience in managing road infrastructure) the right to collect tolls and maintain completed highway stretches for a specified period (typically 20 years) in exchange for an upfront lump sum payment to NHAI. ToT bundles are awarded to the bidder quoting the highest upfront concession fee to collect toll and maintain the roads over the life of the concession. This model is ideal for attracting experienced infrastructure players seeking stable, long-term returns with minimal construction risk.
Key Features:
Flowchart depicting the ToT process:
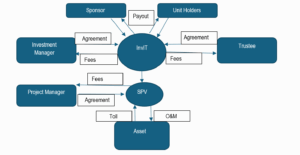
InvITs are collective investment vehicles that enable direct investment of small sums of money from individual and institutional investors in infrastructure projects. InvIT is an innovative financing mechanism that offers stable and predictable cash flows, low risk, liquidity, diversification, and tax benefits to investors. For NHAI, InvITs offer a way to unlock value from a portfolio of assets by pooling them and offering units to investors.
Key Features:
How an InvIT works:
Securitization is another method that NHAI uses to finance major highway projects by converting future toll revenues into immediate funds. Instead of traditional borrowing, they create a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), which essentially sells the rights to future user fees from a project, like a toll road.
NHAI has raised Rs. ~1.4 Lakh Cr. through the above three modes till FY24-25, viz.:
Source: Asset-Monetization Strategy Document
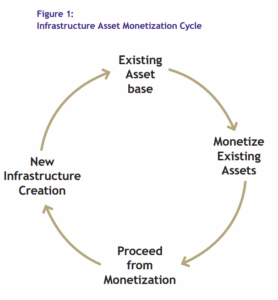
The strategy emphasizes three core pillars: value maximization, transparency, and market development. Through structured identification and valuation of assets, NHAI will ensure that public assets are monetized at their highest potential value. This approach will not only maximize financial returns but also optimize the operational efficiency and longevity of the assets.
The monetization of operational assets provides NHAI with a steady stream of revenue, reducing reliance on traditional funding sources such as government allocations and external debt for financing new projects.